Main Features of Semi Conservative of Dna Replication
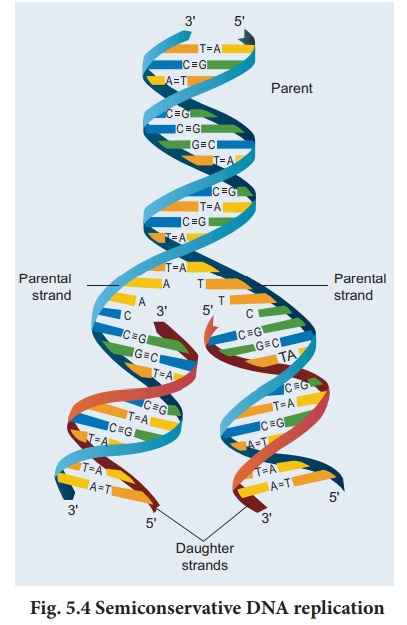
DNA replicates by semi-conservative replication which means that one strand of the parent double helix is conserved in each new. All the available evidence clearly indicates that DNA replication is semiconservative.

The Process Of Semi Conservative Replication 1 5 8 Aqa A Level Biology Revision Notes 2017 Save My Exams
Chain growth in the 5 to 3.
. The separated strands function as templates. Textbook Solutions Expert Tutors Earn. The semi-conservative model is the intuitively appealing model.
This is carried out by the separation of two strands. What Is Conservative DNA Replication. According to the semiconservative model after one round of replication every new DNA double helix would be a hybrid that consisted of one strand of old DNA bound to one strand of newly.
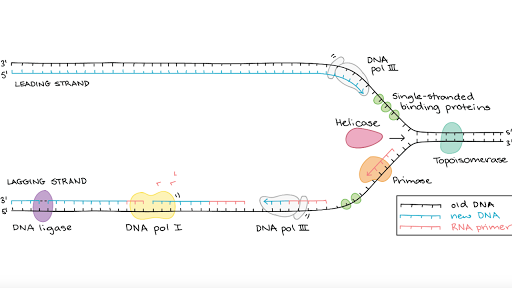
Once the DNA strands have been separated a short piece of RNA called a primer binds to the 3 end of the strand. Coli cells that DNA is replicated. The following are features of DNA replication except.
The primer always binds as the starting point for replication. Start your trial now. In the semi-conservative model the two parental strands separate and each makes a copy of itself.
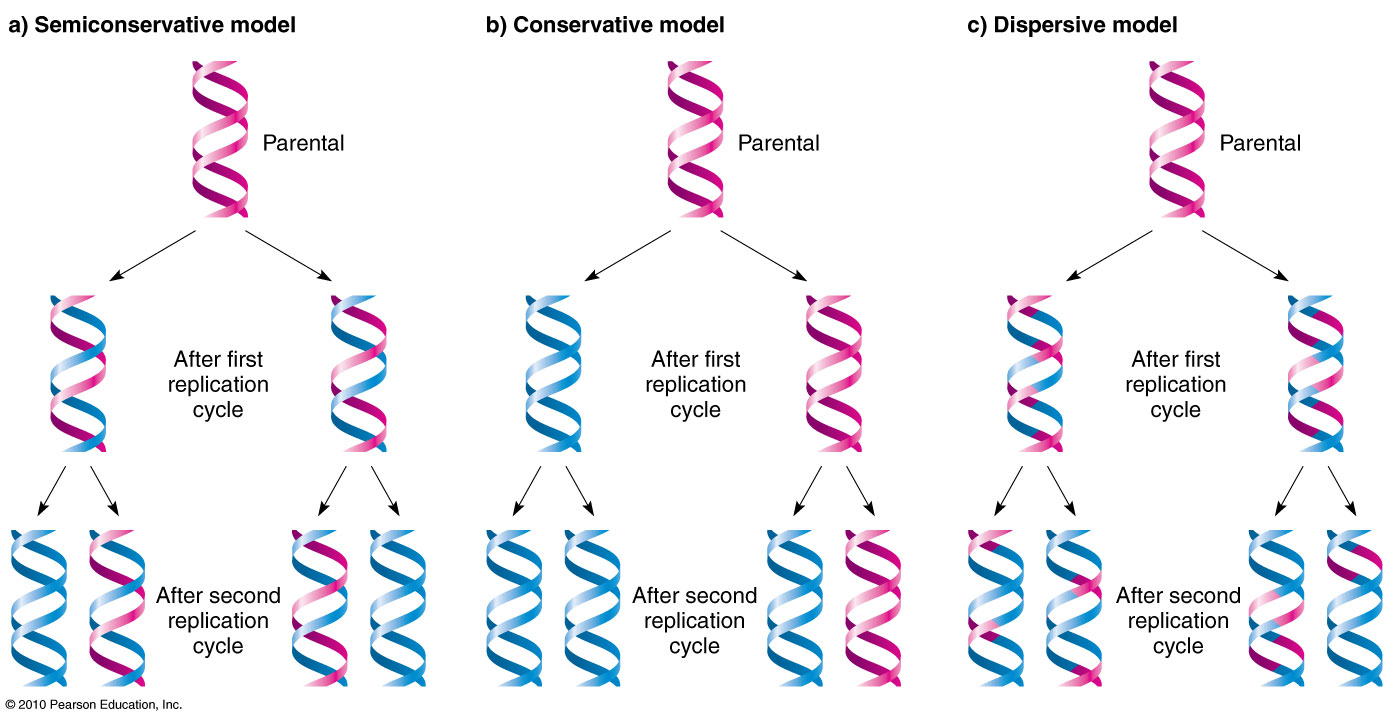
After one round of replication the two daughter molecules each comprises one old and one new strand. In summary DNA replication is the process of making copies of DNA. Replication produces one helix made entirely of old DNA and one helix made entirely of new DNA.
- The 4 types of nucleotide with each of their bases must be present - Both strands of DNA molecule act as template for the attachment of nucleotide - The enzyme DNA polymerase - A source of chemical energy is required to drive the process. DNA Replication The replication of DNA is semi conservative. It then recreates the opposite strand on each of the original strands to form two new identical strands of DNA.
What is required for semi-conservative replication to take place. Semiconservative replication would produce two copies that each contained one of the original strands and one new strand. During DNA replication the double-stranded DNA helix unwinds with the help of the enzyme helicase and the strands are separated.
What Why How Several Facts. Meselson and Stahl Experiment. Primers are generated by the enzyme DNA primase.
This goes through DNA replication and what is meant by semi-conservative replication. DNA is semiconservative because during replication it separates into two strands. Some of the major experimental proofs that DNA replication is semi-conservative they are as follows.
Thus each progeny DNA molecule would consist of one old and one newly synthesized strand. Stages of semi-conservative DNA replication STUDY Flashcards Learn Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity Created by odgersfPLUS Terms in this set 6 step 1 The double helix unwinds and the DNA unzips as hydrogen bonds between the polynucleotides are broken step 2 Existing polynucleotides act as templates for assembly of nucleotides step 3. The following are features of DNA replication except.
DNA has a number of important features that allow semi-conservative replication to take place. Solution for DNA replication is a semi-conservative process. In semiconservative DNA replication each newly synthesized strand of DNA remains associated with the old strand against which it was synthesized.
Experiment carried out by Mathew Messelson and Franklin Stahl 1957-58 conclusively proved that in intact living E. As proposed by Watson and Crick DNA replication is semiconservative a type of replication in which one strand of the daughter duplex is derived from the parent while the other strand is formed anew. The enzyme helicase unwinds and separates the 2 strands of DNA in the double helix by breaking hydrogen bonds between the base pairs.
Semi-Conservative Conservative Dispersive models of DNA replication. Learn the role of DNA helicase and DNA poly. DNA replication is semiconservative meaning that each strand in the DNA double helix acts as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand.
What do you think isare the reasons why most of the clinical features of these diseases involve. DNA Replication The replication of DNA is semi conservative and depends on from NUR FUNDAMENTA at Polytechnic University of the Philippines. DNA is composed of two complementary strands.
A piece of DNA The hydrogen bonds between the bases of the 2 strands of DNA break causing the DNA strands to become separate. Meselson and Stahl experiment 2. State the main functions of the following.
First week only 499. Its not conservative because it does not recreate a whole new strand off of one whole original strand. This is important so that both strands may act as templates for DNA replication.
It does this via the semi-conservative method of DNA replication. If the molar am n. Initially the DNA is present in the form of a double helix comprising 2 polynucleotide strands joined by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases.
This means that half semi of each new DNA strand that is made is made of some of the old DNA so the old DNA is conserved. Once they have been separated from one another each strand can act. DNA bases are held together by weak hydrogen bonds between bases that can be easily broken allowing the two DNA strands to separate2.
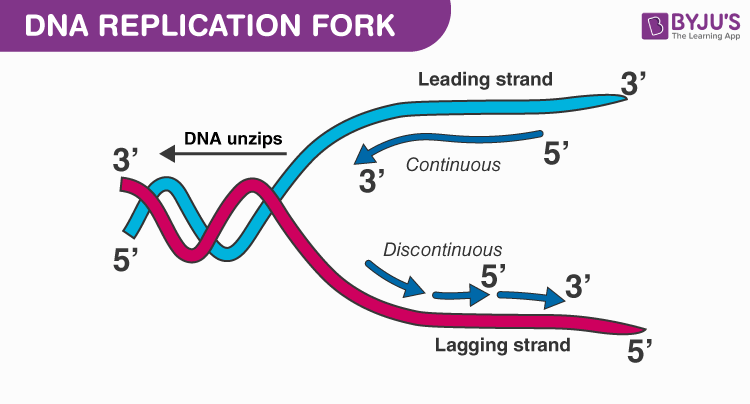
Chain growth in the 5 to 3 direction 15. The leading strand is the simplest to replicate. Replication produces two helices that contain one old and one new DNA strand.
Semi-Conservative Replication Of DNA A Level SL IB Biology - YouTube Hazel explains the semi-conservative mechanism of DNA replication including the role of. Immediately following the discovery of the structure of DNA and the semi-conservative replication of the parental DNA sequence into two new DNA strands it became apparent that DNA replication is organized in a temporal and spatial fashion during the S phase of the cell cycle correlated with the large-scale organization of chromatin in the nucleus. Replication produces two helices in which the individual strands are patchworks of old and new DNA.
Learn how DNA REPLICATES. Conservative replication would leave the two original template DNA strands together in a double helix and would produce a copy composed of two new strands containing all of the new DNA base pairs.

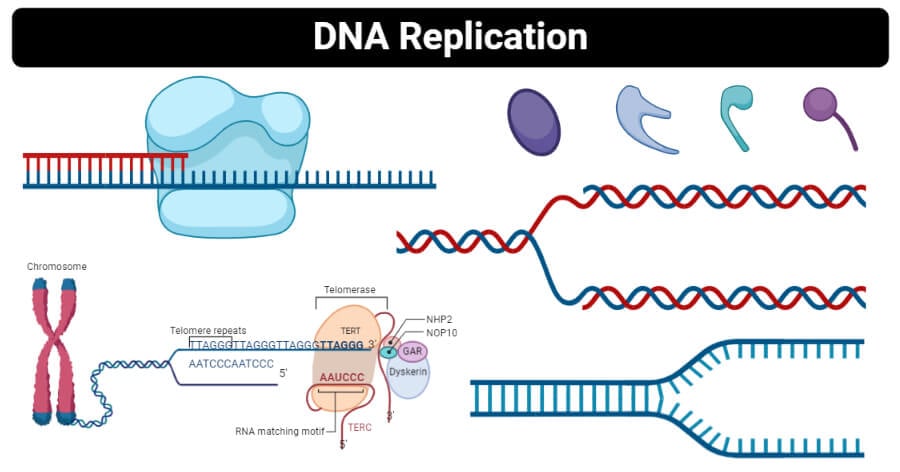
Dna Replication Definition Enzymes Steps Mechanism Diagram
Dna Replication Molecular Genetics

Chapter 9 Dna Replication Chemistry

Dna Replication Structure Stages Of Replication Teachmephyiology
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy

Leading And Lagging Strand Dna Replication Dna Molecular Biology

Dna Replication Steps Diagram Expii

7 2 Semi Conservative Dna Replication Biology Libretexts
Dna Replication Process With Diagrams Class 12 Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Dna Replication
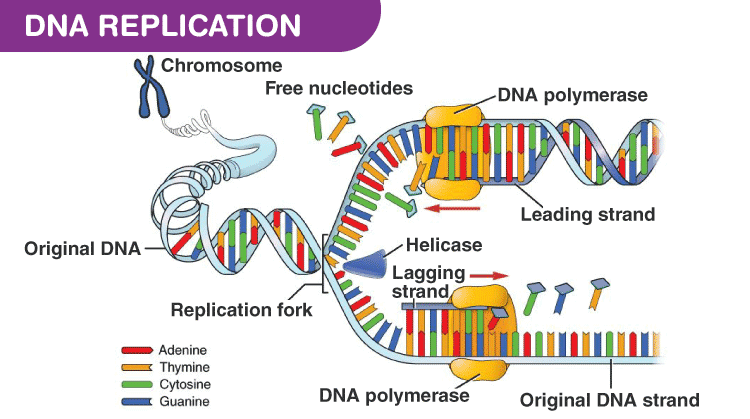
Dna Replication Process With Diagrams Class 12 Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Dna Replication

General Features Of Dna Replication
![]()
Semiconservative Dna Replication Wall Art Canvas Prints Framed Prints Wall Peels Great Big Canvas
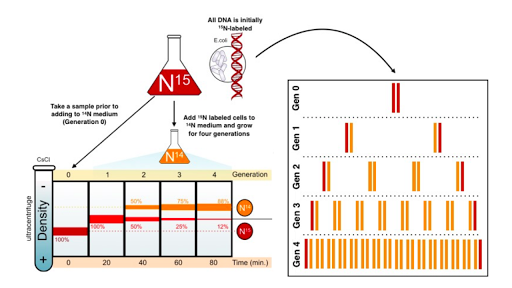
Mode Of Dna Replication Meselson Stahl Experiment Article Khan Academy

What Are The Steps Of Dna Replication
Dna Replication Is Semi Conservative Labxchange
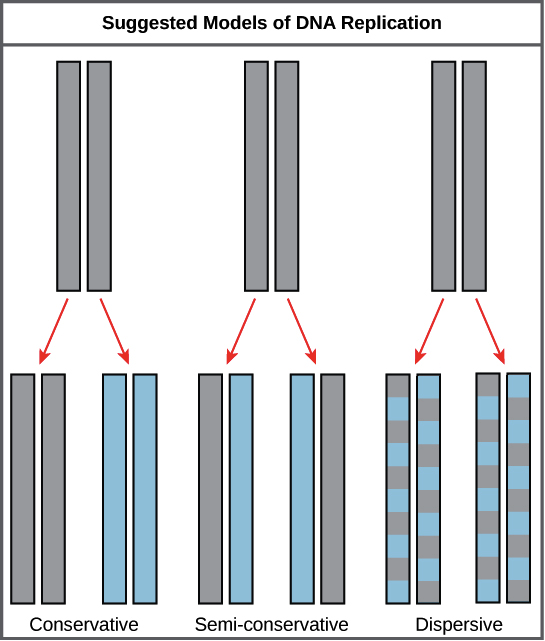
Mode Of Dna Replication Meselson Stahl Experiment Article Khan Academy
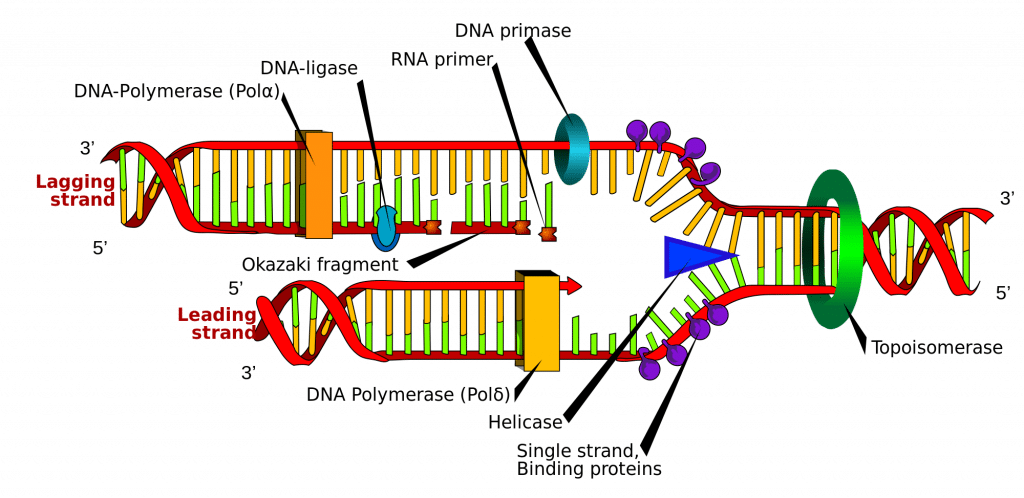
Dna Replication Structure Stages Of Replication Teachmephyiology

Comments
Post a Comment